VEGF Signaling
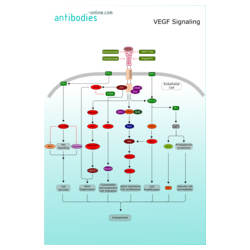
Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) constitute a sub-family of growth factors that stimulate the growth of new blood vessels. VEGFs are important signaling proteins and initiate angiogenesis via several signalling cascades. All members of the VEGF family stimulate cellular responses by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors (VEGFRs) on the cell surface. VEGFR-2 appears to mediate almost all of the known cellular responses to VEGF1. After receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation, several SH2 domain-containing signal transduction molecules are activated such as PLC-γ), VRAP (VEGF Receptor-Associated Protein), Sck, and Src2.
PLC-Gamma catalyzes the hydrolysis of PIP2 (Phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-Bisphosphate), creating IP3 (Inositol Trisphosphate) and DAG (Diacylglycerol), which stimulate the release of Ca2+ from internal stores. Ca2+ release promotes NO (Nitric Oxide) production via NOS (Nitric Oxide Synthase) as well as activativation PKC (Protein Kinase-C). NO regulates hematopoiesis and modulates cell growth.Together with PKC activation via DAG, the formation of SHC-GRB2-SOS complex enables the Raf1-MEK-ERK pathway3. Cell survival signal is mainly mediated through PI3K-mediated activation of Akt/PKB (Protein Kinase-B). BAD as well as Caspase-9 can inactivate Akt/Pkb ultimately leading to apoptosis instead of cell survival. p38 pathway transduces the VEGF information concerning Actin organization via MAPKAPK2/3 (MAP Kinase Activated Protein Kinase-2/3) and phosphorylation of the F-Actin polymerization modulator, HSP27 (Heat Shock Protein-27). The activation of PTK2 and Paxillin over VEGFR2 leads to recruitment Talin and Vinculin to the focal adhesion plaque4. These Actin-anchoring proteins further support actin reorganization5.
When VEGF is overexpressed, it can contribute to disease. Cancers that can express VEGF and establish blood supply are able to grow and metastasize. Another possible result are vascular disease in the retina of the eye and other parts of the body. Drugs such as Pegaptnib, Bevacizumab, and Ranibizumab can inhibit VEGF and control or slow those diseases.
References:
- Matsumoto T, (2001): “VEGF receptor signal transduction”. Sci STKE, 112:re21 [PMID: 11741095]
- Li-Wha Wu(1999): “VRAP Is an Adaptor Protein That Binds KDR, a Receptor for Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor. ” J. Biol. Chem., 275, 6059-6062 [DOI: 10.1074]
- Harmer SL(1997): "Shc contains two Grb2 binding sites needed for efficient formation of complexes with SOS in B lymphocytes.” Mol Cell Biol, Jul;17(7):4087-95. [PMID: 9199344]
- Brian P.(2002): “Src-mediated coupling of focal adhesion kinase to integrin αvβ5 in vascular endothelial growth factor signaling ” Mol Cell endocrinol, 217(1-2):67-74.. [PMID: 2173263]
- Ganju RK (1998): “Human immunodeficiency virus tat modulates the Flk-1/KDR receptor, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and components of focal adhesion in Kaposi's sarcoma cells. ” J Virol., Jul;72(7):6131-7. [PMID: 9621077]